Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS cells): ความก้าวหน้าและศักยภาพในอนาคต
iPS cells คือ เซลล์ที่ถูกเปลี่ยนแปลงจากเซลล์ธรรมดาของร่างกายให้เจริญย้อนกลับกลายเป็นเซลล์ตั้งต้น (stem cells) ที่สามารถพัฒนาเป็นเซลล์ชนิดต่าง ๆ ในร่างกายได้ ซึ่งการวิจัยนี้ค้นพบโดยนักวิทยาศาสตร์ ชินยะ ยามานากะ ในปี 2006 และทำให้ได้รับรางวัลโนเบลสาขาการแพทย์ในปี 2012
วิธีการสร้าง iPS cells
เริ่มจากการนำเซลล์ทั่วๆ ไปในร่างกาย เช่น เซลล์ผิวหนังหรือเซลล์เม็ดเลือด มาใส่ยีนพิเศษ (reprogramming factor) ที่ทำให้เซลล์เหล่านี้เจริญย้อนกลับไปเป็น stem cells ซึ่งสามารถทำได้โดยวิธีการการใช้ไวรัสหรือไม่ใช้ไวรัส หลังจากนั้น iPS cells เหล่านี้ก็จะมีความสามารถในการแบ่งตัวแบบไม่สิ้นสุด และมีคุณสมบัติเหมือนกับ stem cells ที่ได้มาจากตัวอ่อนนั่นเอง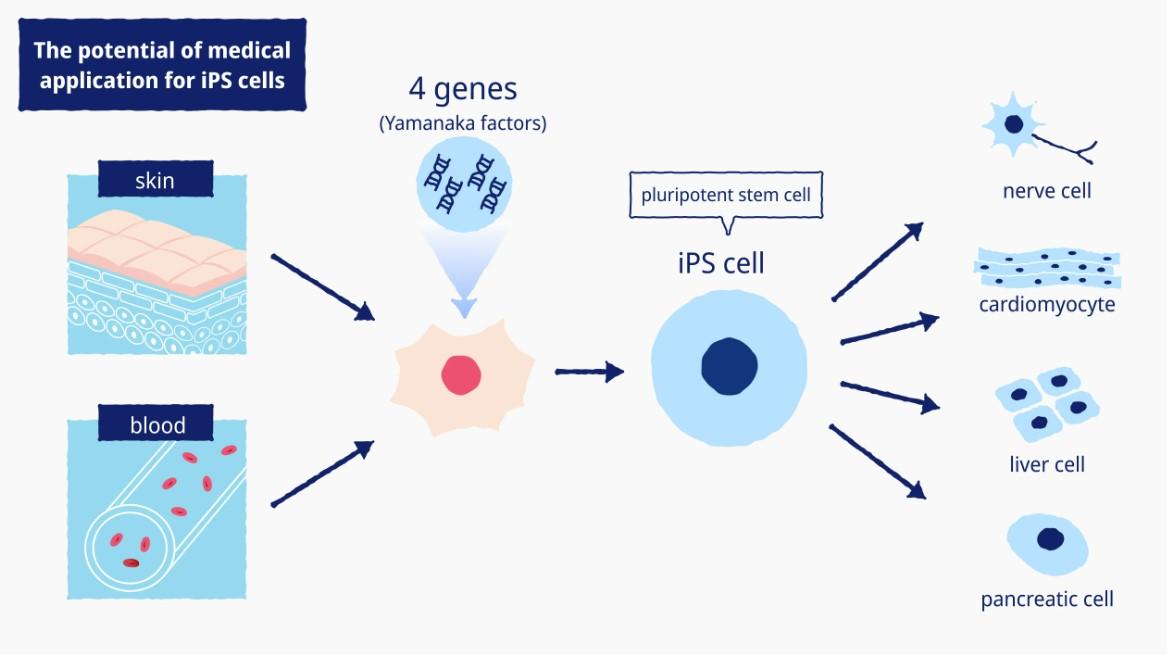
ประโยชน์ของ iPS cells
- การฟื้นฟูร่างกาย: นำมาประยุกต์ใช้ในการสร้างเนื้อเยื่อและอวัยวะใหม่ๆ ภายในร่างกาย เช่น สร้างเซลล์ประสาทสำหรับผู้ป่วยที่มีปัญหาสมอง หรือสร้างเซลล์หัวใจสำหรับผู้ป่วยโรคหัวใจขาดเลือด
- การศึกษาโรค: ช่วยให้นักวิทยาศาสตร์สร้างแบบจำลองของโรคในห้องปฏิบัติการ เพื่อศึกษาและเข้าใจโรคได้ดียิ่งขึ้น เช่น โรคทางพันธุกรรม
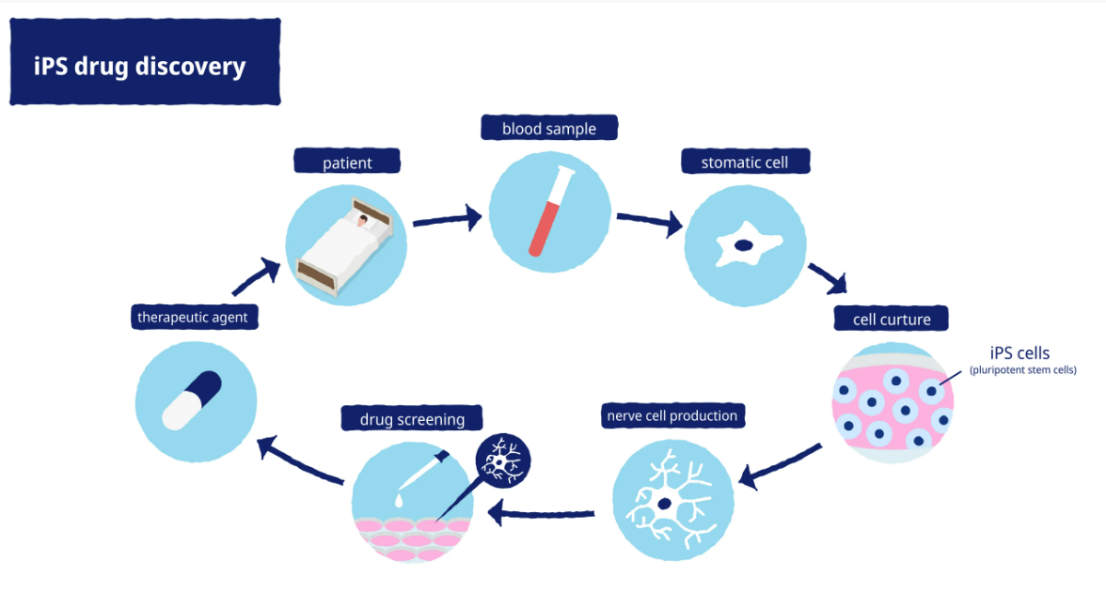
- การทดสอบยา: iPS cells ถูกนำมาใช้ในการทดสอบยาตัวใหม่และดูผลการรักษาในระดับตัวบุคคลได้ เพื่อดูว่ายามีประสิทธิภาพและปลอดภัยแค่ไหน
ความท้าทายและอนาคตของ iPS cells
ความท้าทายของการเลี้ยง iPS cells คือการรักษาเสถียรภาพของเซลล์ในระยะยาว และความเสี่ยงของการเกิดเนื้องอกในอนาคต ดังนั้นการวิจัยจะเน้นไปที่การทำให้ iPS cells ปลอดภัยและมีประสิทธิภาพมากขึ้น เพื่อใช้ในการรักษาโรค ทั้งนี้การนำ iPS cells มาใช้ในการรักษายังคงอยู่ในการวิจัยและเป็นแพทย์ทางเลือกในปัจจุบัน
Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS cells): Progress and future potential
iPS cells are cells that have been reprogrammed from normal body cells to convert to a pluripotent state, they can develop into various types of cells within the body. This research was discovered by scientist Shinya Yamanaka in 2006, and it earned him the Nobel Prize in Medicine in 2012.
How to generate iPS cells
The process starts with taking normal body cells, such as skin cells or blood cells, and introducing special genes known as reprogramming factors. These factors cause the cells to convert to a stem cell state. This can be achieved using viral or non-viral methods. Once created, iPS cells have the ability to divide indefinitely and possess characteristics similar to embryonic stem cells.
Benefits of iPS cells
- Tissue regeneration: iPS cells can be applied to regenerate tissues and organs within the body. For example, they can be used to create neural cells for patients with brain issues or heart cells for those with ischemic heart disease.
- Disease research: They allow scientists to create disease models in the laboratory, which helps in better understanding diseases, including genetic disorders.
- Drug testing: iPS cells can be used to test new drugs and observe their effects at the individual level, ensuring their efficacy and safety.
Challenges and future of iPS cells
The challenges of culturing iPS cells include maintaining their long-term stability and the potential risk of tumor formation. Therefore, research focuses on making iPS cells safer and more effective for therapeutic use. Currently, the application of iPS cells in treatment remains under research and is considered an alternative medical approach.